You might be wondering what an air handling unit, or AHU, is for. Well, imagine a system that takes care of everything to ensure the air you breathe at home or at work is pleasant and healthy. The AHU is a bit like the lungs of your building. It takes outside air, cleans it, adjusts its temperature and humidity, and then redistributes it. It’s quite a complex piece of equipment, but its role is truly important for your comfort and health.
Key Points to Remember
- The AHU improves indoor air quality by filtering pollutants and allergens, which is good for your health.
- It regulates temperature and humidity for optimal comfort, regardless of the season.
- Main components like filters, fans, and heat exchangers work together to treat the air.
- There are different types of AHUs, such as single-flow and double-flow models, each with its specific features.
- Proper maintenance of your AHU is necessary for it to function well and continue to provide you with healthy air.
The essential role of the AHU in air treatment

An air handling unit, often abbreviated as AHU, is central equipment in managing the indoor environment of many buildings. Its role goes far beyond simple ventilation; it is designed to actively modify air characteristics to meet specific needs for comfort, health, and safety. In short, it acts as the respiratory system of a building, ensuring that the air you breathe is of the best possible quality.
Improvement of indoor air quality
One of the most important aspects of an AHU’s work is to ensure healthy indoor air. This begins with the introduction of fresh outdoor air, which replaces stale and potentially pollutant-laden air. The drawn-in air then passes through several filtration stages. These filters are designed to capture a wide range of particles, from large dust particles to finer allergens like pollen, and even some microscopic particles. For more demanding environments, high-efficiency filters, such as HEPA filters, can be used to retain up to 99.95% of the finest particles. By eliminating these contaminants, the AHU directly contributes to reducing the risks of allergies, respiratory problems, and improving the general well-being of occupants.
Thermal regulation and occupant comfort
Beyond purification, the AHU plays a major role in maintaining a pleasant temperature and humidity level. Thanks to its heat exchangers, it can heat or cool the air as needed, thus creating a stable indoor climate throughout the year. Furthermore, integrated humidification and dehumidification systems allow for adjusting the air’s humidity level. A well-regulated humidity level is essential not only for comfort but also to prevent the proliferation of certain microorganisms and protect sensitive materials. This ability to precisely control ambient conditions is particularly important in places like hospitals or laboratories, where a controlled environment is a necessity.
Health safety in sensitive environments
In environments where controlling health risks is paramount, such as healthcare facilities, research laboratories, or cleanrooms, the role of the AHU is even more critical. It allows for controlling air pressure between different zones, thus preventing the spread of contaminants or pathogens. For example, in an operating theatre, a slight overpressure of fresh air compared to adjacent areas prevents potentially contaminated air from entering. Moreover, some AHUs are equipped with systems capable of neutralising bacteria or odours, thereby enhancing the safety and hygiene of the premises. The AHU’s ability to manage the mix between fresh air and recirculated air, while ensuring thorough filtration, is a key component of building safety.
Understanding how an air handling unit works
To fully grasp the role of an air handling unit (AHU), you need to understand how it works. Imagine it as the respiratory system of your building. It takes outdoor air, cleans it, heats or cools it, adjusts its humidity, and then distributes it where needed. It’s quite a complex process, but once you know the steps, everything becomes clearer.
The air treatment cycle
The path of air in an AHU follows a well-defined sequence. First, outdoor air is drawn in. Then, it passes through a series of filters to remove dust, pollen, and other particles. After this purification, the air can be heated or cooled using heat exchangers, and then its humidity level is adjusted if necessary. Finally, fans propel this treated air into the building via a network of ducts. This complete cycle aims to provide healthy and comfortable indoor air.
Principle of air circulation regulation
Air circulation regulation is at the heart of an AHU’s operation. It ensures that the correct volume of air is moved at the right time. This is achieved through fans whose speed can be adjusted, and dampers that control flow rates. The objective is to maintain constant pressure and ventilation in different areas of the building, which is essential for comfort and air quality. You can learn more about ventilation systems in this home automation guide.
Management of the mix between fresh air and recirculated air
An important part of an AHU’s job is to manage the mix between fresh air coming from outside and air already present in the building (recirculated air). This mix is crucial for several reasons. It allows for renewing indoor air by bringing in fresh oxygen while expelling stale air. Furthermore, by mixing fresh air with recirculated air, which is often already at a more comfortable temperature, the AHU can reduce its energy consumption for heating or cooling. The proportion of each type of air is adjusted by specific dampers in a mixing box.
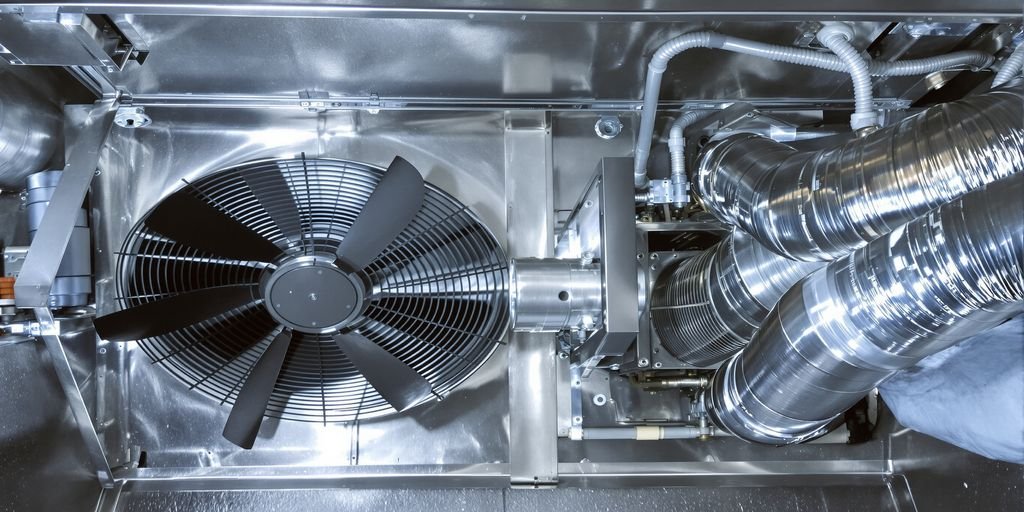
The fundamental components of an AHU
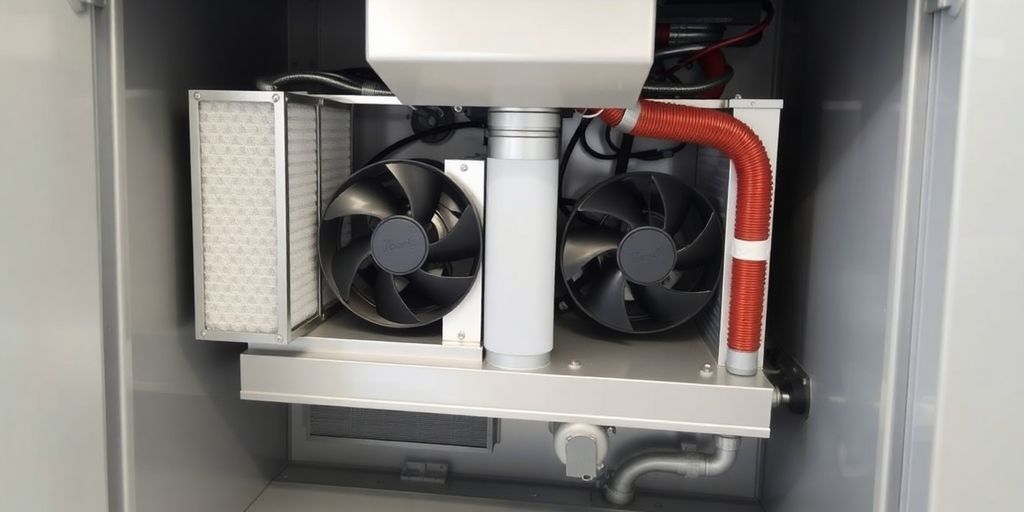

An air handling unit (AHU) is complex equipment whose proper functioning relies on the interaction of several key components. Each of these elements plays a precise role in the purification, thermal regulation, and circulation of air within your building.
Air filters for purification
Filters are the first line of defence against pollutants. They retain fine particles, dust, pollen, and other allergens present in the air. Depending on the required level of purity, you can find several filtration stages, ranging from pre-filters for large particles to HEPA filters that capture up to 99.95% of the finest particles. Proper maintenance of these filters is essential to maintain good indoor air quality and system efficiency.
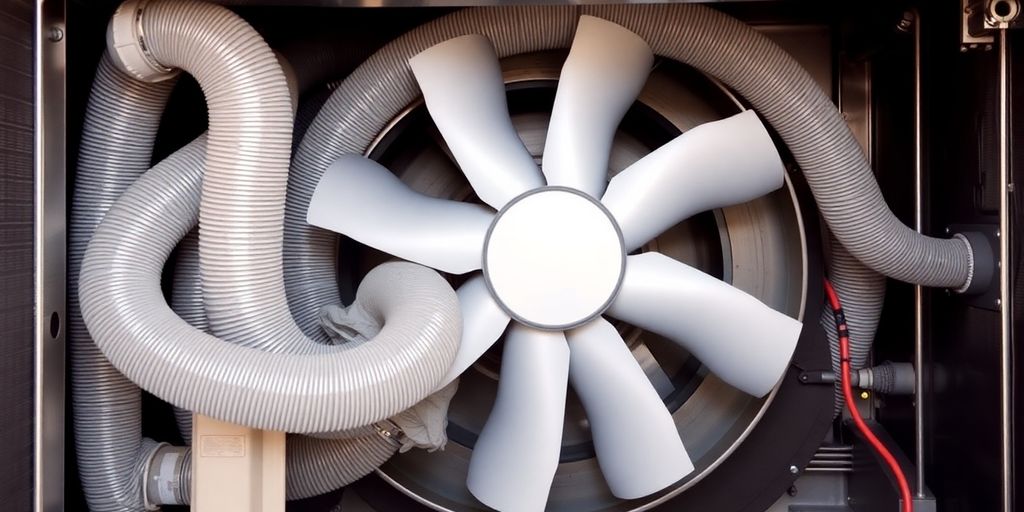
Fans for circulation
Fans are the engine of the AHU. They ensure the propulsion of air throughout the entire system, from the intake of fresh air to its diffusion into the premises, passing through the various treatment stages. The power and type of fan are chosen according to the required airflow and the pressure losses in the air duct network. They are often equipped with variable speed motors to adjust the airflow as needed.
Heat exchangers for regulation
These components are essential for controlling air temperature. They come in the form of coils (hot or cold) through which a heat transfer fluid (hot water, chilled water, or refrigerant) circulates. As air passes through these coils, its temperature is modified to reach the desired set point. This is how the AHU ensures the heating or cooling of the supplied air.
Humidification and dehumidification systems
For optimal comfort, the AHU can integrate systems to adjust the air’s humidity level. Humidifiers add water vapour when the air is too dry, while dehumidifiers remove excess humidity, for example, by condensation. These functions are particularly important in environments where humidity control is critical, such as in certain industrial processes or healthcare facilities. Condensation management, for instance, requires a water recovery system like the one described in this recovery system.
Understanding the role of each component allows you to appreciate the complexity of air management and the importance of regular maintenance to guarantee the overall performance of your installation. A good knowledge of these elements can also help you better understand the settings of your home automation system if your AHU is connected to it.
Specific functions performed by the AHU
An air handling unit (AHU) does not merely circulate air; it actively transforms it to meet precise requirements. These specific functions are at the heart of its usefulness, whether for general comfort or for more technical applications.
Introduction of fresh air and extraction of stale air
The primary role of an AHU is to renew indoor air. It captures outdoor air, filters it, and then distributes it into the premises. Simultaneously, it extracts stale air, laden with CO₂, humidity, or pollutants, to discharge it outside. This cycle ensures constant air quality and prevents the accumulation of undesirable substances. This renewal is vital for the health and well-being of occupants.
Thermal treatment and humidity adjustment
Beyond simple renewal, the AHU actively adjusts the temperature and humidity level of the air. Thanks to heat exchangers, it can heat the air in winter and cool it in summer. Similarly, humidification or dehumidification systems are integrated to maintain an optimal humidity level, often critical in environments such as hospitals or laboratories. Trane air handling units, for example, offer customised solutions for these adjustments, adapting to your specific needs [b849].
Energy recovery for efficiency
A particularly interesting function of modern AHUs, especially double-flow ones, is energy recovery. Before discharging stale air outside, the AHU can extract some of its heat. This recovered heat is then used to preheat the incoming fresh air. This process significantly reduces the energy consumption required for heating, making the system more economical and ecological.
Different types of air handling units
There are several configurations of air handling units (AHUs), each adapted to specific needs in terms of ventilation and air conditioning. Understanding these distinctions will help you choose the most appropriate solution for your installation.
Single-flow units
Single-flow air handling units manage a single airflow. They can either only introduce fresh air, or only extract stale air, or manage a mix of both without significant energy recovery. This type of system is often used in applications where air renewal is the main priority, without requiring complex thermal treatment or indoor air recycling. They are generally simpler and less expensive to install.
Double-flow units
Double-flow units, on the other hand, simultaneously manage two airflows: the supply of fresh outdoor air and the extraction of stale indoor air. The major distinction within this category lies in the presence or absence of an energy recovery system. Double-flow systems with energy recovery are equipped with a heat exchanger that transfers heat (and sometimes humidity) from the extracted air to the incoming fresh air. This energy recovery significantly reduces the building’s overall energy consumption, especially for heating in winter and cooling in summer. These systems are widely used in modern commercial buildings and industrial facilities concerned with their energy efficiency. There are also decentralised AHUs, which are small units installed directly in the areas to be treated, offering a more localised solution.
Various operating modes
Beyond the single or double-flow configuration, AHUs can operate in different modes to adapt to climatic conditions and occupant needs. These modes may include:
- Cooling only mode: used when only air conditioning is needed.
- Predominantly cooling mode: the system prioritises cooling, but can also provide supplementary heating.
- Balanced heating/cooling mode: the system adjusts the temperature neutrally, without prioritising heating or cooling.
- Predominantly heating mode: the system prioritises heating, with a possibility of supplementary cooling.
The choice of operating mode will depend on the season, the occupancy of the premises, and the desired settings for thermal comfort. The management of these modes is often integrated into a centralised control system, much like the brain of a smart home.
The selection of an AHU must take into account not only the air treatment capacity but also energy efficiency and the flexibility of operating modes to meet the specific requirements of each project. A good understanding of these aspects is comparable to how a home automation hub coordinates the different devices in a smart home.
Optimisation and maintenance of the AHU
For your air handling unit (AHU) to function optimally and continue to provide you with healthy air, particular attention to its optimisation and maintenance is essential. It’s not enough to install it; you also need to take care of it.
Defining needs and sizing
Even before thinking about maintenance, it’s important to ensure that your AHU is correctly sized. An undersized system will never be able to meet the real needs of your building, while an oversized system will consume energy unnecessarily. Several elements must be considered for proper sizing: the volume of the rooms to be treated, the number of people staying there, the activities taking place, and specific air quality requirements. A precise calculation of the necessary fresh air flow rate is the basis for choosing the right fan size and the capacity of other components. Good initial planning, like what our experts can help you achieve, is the first step towards lasting performance. Define your needs
Importance of explanatory diagrams
Understanding how your AHU works often involves analysing diagrams. These visual representations detail the air path, the role of each component (filters, fans, heat exchangers, etc.), and their interactions. Knowing how to read these diagrams helps you better understand the settings, identify potential malfunctions, and communicate more effectively with maintenance technicians. They are key to grasping the internal logic of your ventilation system.
Component maintenance for performance
Regular maintenance is the cornerstone of your AHU’s longevity and efficiency. This involves a series of preventive and corrective actions. Here are the essential points to monitor:
- Air filters: Their periodic replacement is non-negotiable. Clogged filters reduce airflow, increase fan energy consumption, and decrease the quality of filtered air. There are different levels of filtration, from pre-filters to HEPA filters, each with a specific lifespan and impact.
- Fans: Check their proper functioning, the absence of abnormal noises, and the cleanliness of the blades. A well-maintained fan ensures optimal air circulation.
- Heat exchangers: Ensure they are not obstructed by dust or limescale, which would reduce their ability to heat or cool the air efficiently. Cleaning the coils (hot water, chilled water) is a common task.
- Humidification/dehumidification systems: These components require particular attention to maintain the desired humidity level, especially in sensitive environments.
Proactive maintenance, based on usage cycles and manufacturer recommendations, is the best approach to ensure flawless operation and continuous optimisation of your equipment. Daily maintenance is often key.
By following these recommendations, you ensure that your AHU continues to fulfil its role effectively, contributing to a healthy and comfortable indoor environment, while controlling your energy consumption.
In summary: the importance of your AHU
There you have it, you now know what an air handling unit is and what it’s for. It’s truly a key element for having healthy air and a pleasant temperature at home or in your workplace. By understanding its operation and components, you can better appreciate its role. Think about it next time you feel good in a space, there’s a strong chance your AHU has something to do with it. It’s a bit like the silent engine of your indoor comfort.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an air handling unit?
An air handling unit, also known as an AHU, is a machine that manages the air in a building. It makes it cleaner, heats or cools it, and ensures there’s always enough fresh air for you to breathe well. It’s a bit like your home’s ventilation and air conditioning system, but more sophisticated.
How does an air handling unit work?
Imagine that outdoor air enters the AHU. First, it passes through filters to remove dust and small particles that can be bad for your health. Then, depending on the need, it is heated or cooled. Sometimes, humidity is also added or removed. Finally, this clean air at the right temperature is sent into the rooms through ducts.
What is the role of an air handling unit?
The main role of the AHU is to make the air you breathe inside buildings healthier and more comfortable. It helps prevent allergies by filtering pollen, it maintains a pleasant temperature so you’re neither too hot nor too cold, and it ensures that fresh air always comes in and stale air goes out.
What are the main components of an air handling unit?
An AHU is made up of several important parts. There are filters to clean the air, fans to circulate the air, heat exchangers (which are like miniature radiators or air conditioners) to change the temperature, and sometimes systems to add or remove humidity.
What are the different types of air handling units?
There are mainly two types: single-flow, which manage either the incoming or outgoing air, and double-flow, which do both at the same time. Double-flow units are often more efficient because they can recover heat from the outgoing air to warm the incoming air, which saves energy.
Why is it important to maintain an air handling unit?
For an AHU to work well and for a long time, it needs regular maintenance. This means cleaning or changing filters, checking that the fans are running correctly, and that the heating and cooling systems are working properly. Good maintenance ensures consistently healthy air and prevents breakdowns.